Overview
Contents in this page
What is the SAFE framework?
What is the purpose of the SAFE framework?
The SAFE framework encourages the food industry to uphold good food safety standards to retain and build consumer trust. Consumers can also make more informed dining choices by referring to SAFE grades and supporting food establishments that prioritise food safety.
What types of food establishments does the SAFE framework apply to?
The SAFE framework applies to SFA-licensed food establishments that process or prepare food for sale to the public. These food establishments are grouped into two categories.
Licensees can check their establishment category by scanning the QR code on their SFA licence to access their business trade description, then matching this description with the establishments listed in the tables below.
Category 1 Food Establishments
These include restaurants with kitchen size of 16m² or more, caterers, central kitchens and food manufacturing premises, whose establishments are involved in significant processing or preparation of food. More details are in the table below.
| Category 1 Food Establishments | |
|---|---|
| Restaurants & Catering Services |
|
| Food Manufacturing & Processing |
|
Category 2 Food Establishments
These include restaurants with kitchen size less than 16m², cold stores, takeaway outlets, supermarkets, and food stalls in coffee shops, canteens, food courts and hawker centres, whose establishments engage in low/moderate levels of food processing or preparation. More details are in the table below.
| Category 2 Food Establishments | |
|---|---|
| Retail Food Shops |
|
| Mobile Food Services |
|
| Food Stalls |
|
| Others |
|
SFA-licensed food establishments that are not directly involved in the processing or preparation of food are excluded from the SAFE framework. These include:
- Main operators of canteens, coffee shops, food courts and private markets (Note: Individual food stalls within these establishments are still covered under SAFE Category 2)
- Market stalls selling raw seafood, meat and other market produce items
How are the grades determined under the SAFE framework?
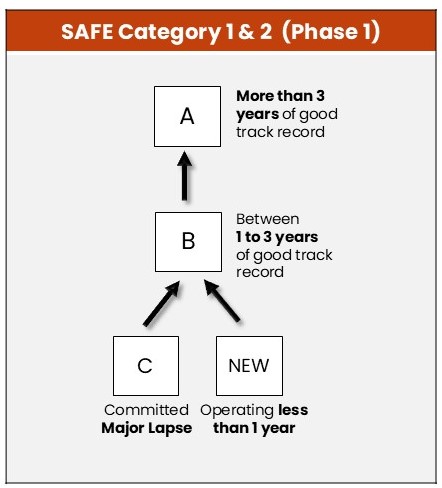
Phase 1 (implemented on 19 Jan 2026)
Phase 1 (implemented on 19 January 2026)
Fast-track* option is available for Category 1 food establishments to attain grade ‘A’ in shorter time. They must have a 1-year good food safety track record, appoint an Advanced Food Hygiene Officer (AFHO) and implement a certified FSMS. There is no fast-track option for Category 2 establishments.
SAFE grades will be updated based on food establishments’ food safety track records. For instance, if a food establishment commits a major lapse, it will be immediately downgraded to grade ‘C’, regardless of the present grade.
*Not applicable for food establishments with grade ‘C’ track record (i.e., committed major lapse)
| Grade | Category 1 Food Establishment | Category 2 Food Establishment |
|---|---|---|
| A | Good track record (i.e. no major lapse) for more than three years | |
Fast-track to grade 'A' if establishment has: | No fast-track option | |
| B | Good track record (i.e. no major lapse) of between one to three years | |
| New | In operation for less than one year | |
| C | Committed major lapse (e.g. court conviction or suspension of licence under the Points Demerit System) regardless of present grade | |
What is the role of an Advanced Food Hygiene Officer?
- Workforce Skills Qualification (WSQ) Food Safety Course (FSC) Level 4, or
- Former WSQ Apply Food Safety Management Systems for Food Service Establishments Course*
Phase 2
Phase 2 (implementation details to be announced by 2027)
Grades will continue to be determined by the food establishment’s food safety track records. In addition, Category 1 food establishments who wish to maintain or attain grade ‘A’, would need to meet additional requirements as shown in the table below.
| Grade | Category 1 Food Establishment | Category 2 Food Establishment |
|---|---|---|
| A | Good track record (i.e. no major lapse) for more than three years | Good track record (i.e. no major lapse) for more than three years |
Can fast-track to grade 'A' if establishment has: | No fast-track option | |
| B | Good track record (i.e. no major lapse) for between one to three years | |
| New | In operation for less than one year | |
| C | Committed major lapse (e.g. court conviction or suspension of licence under the Points Demerit System) regardless of present grade | |

FAQs
Contents in this page
Why are new entrants graded as ’NEW’ instead of grade ‘B’?
Is there any change to the Points Demerit System (PDS)?
Will my grade be affected if there is a change in licensee or management?
What should I do with the old grade decals from the previous grading system?
What does the Food Safety Management System (FSMS) cover?
- Implementing programmes and practices that establish and maintain a baseline hygienic environment for the processing and preparation of food (e.g., cleaning and sanitation programmes, pest control plan).
- Applying the principles of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP), which helps to identify and control food safety risks at key stages of food preparation. This involves monitoring critical points in food processing or preparation and setting safety limits that must be maintained at these points.
- Maintaining proper and accurate records, which is crucial for the monitoring of FSMS and the quick identification and rectification of any food safety issues. It also allows for the traceability of hazards to the contamination source to identify the root cause of any food safety incidents.
What is the difference between a non-certified and a certified FSMS? Is certified FSMS required under the SAFE framework?
A non-certified FSMS refers to an organisation’s FSMS that is:
- Drawn up based on a company's or food establishments’ in-house standards and
- Based on non-certifiable standards such as SS583:2022.
A certified FSMS refers to an organisation’s FSMS that is assessed and verified by a certification body, which is accredited by:
- Singapore Accreditation Council (SAC), which include Singapore Standards - SS444, SS590 and ISO 22000;
- Bodies who are signatories of the International Accreditation Forum (IAF) multilateral recognition arrangement (MLA) for ISO 22000 and FSSC 22000; or
- Brand Reputation Compliance Global Standards (BRCGS)-recognised accreditation bodies which are signatories of the IAF MLA
More information on the FSMS requirements and implementation are available at Understanding the Food Safety Management System.
A certified FSMS is required for Category 1 food establishments to fast-track to grade ‘A’, in addition to appointing an Advanced Food Hygiene Officer, and having a one-year good food safety track record.
For more information
You can contact us via the SFA Online Feedback Form.
